Predictive Imputation

Summary
A robust data engineering tool developed to handle missing data through custom K-means clustering and automated classification, optimizing predictive accuracy across varied datasets using Python.
Details
This project addressed a critical challenge in data science: maintaining dataset integrity when faced with incomplete information. I engineered a two-stage pipeline—Missing Value Estimation and Optimal Classification—to automate the cleaning and predictive analysis of high-dimensional datasets. The software architecture was designed to perform sophisticated data preprocessing and model selection using a combination of Pandas, NumPy, and Scikit-learn.
Advanced Missing Value Estimation
Data imputation was approached through two distinct methodologies to compare the impact of local vs. global mean substitution.
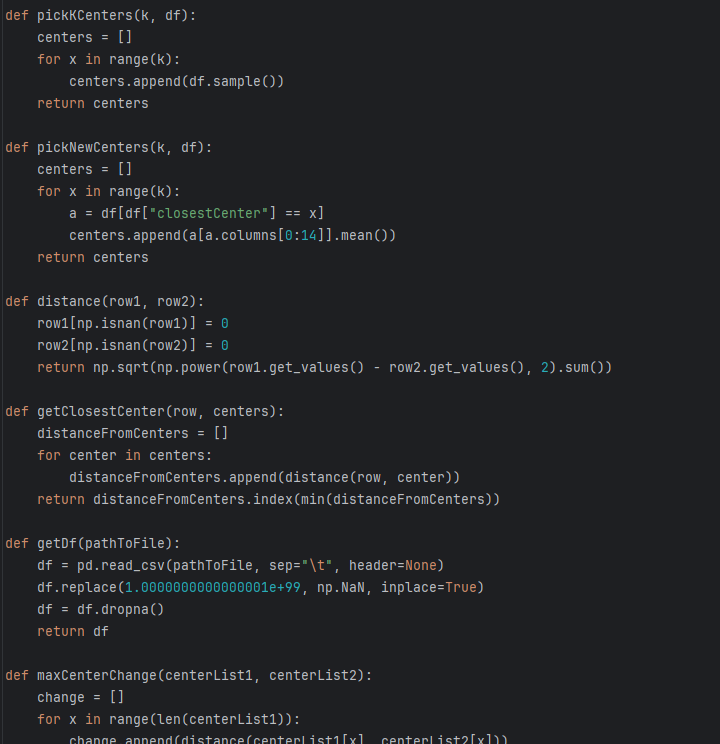
- Basic Mean Imputation: Implemented a global strategy using
df.fillna(df.mean())to replace null values with the column-wide average. - K-Means Cluster Imputation: Developed a more localized approach by implementing a custom K-means algorithm to group similar data points.
- Centroid Optimization: Built functions to initialize (
pickKCenters) and iteratively update (pickNewCenters) centroids based on Euclidean distance. - Group-Based Filling: For rows with missing data, the system identifies the closest cluster and replaces null values with the mean specific to that cluster, preserving local data variance.
- Centroid Optimization: Built functions to initialize (
Feature Engineering and Preprocessing
Before classification, raw data undergoes a rigorous cleaning and transformation phase:
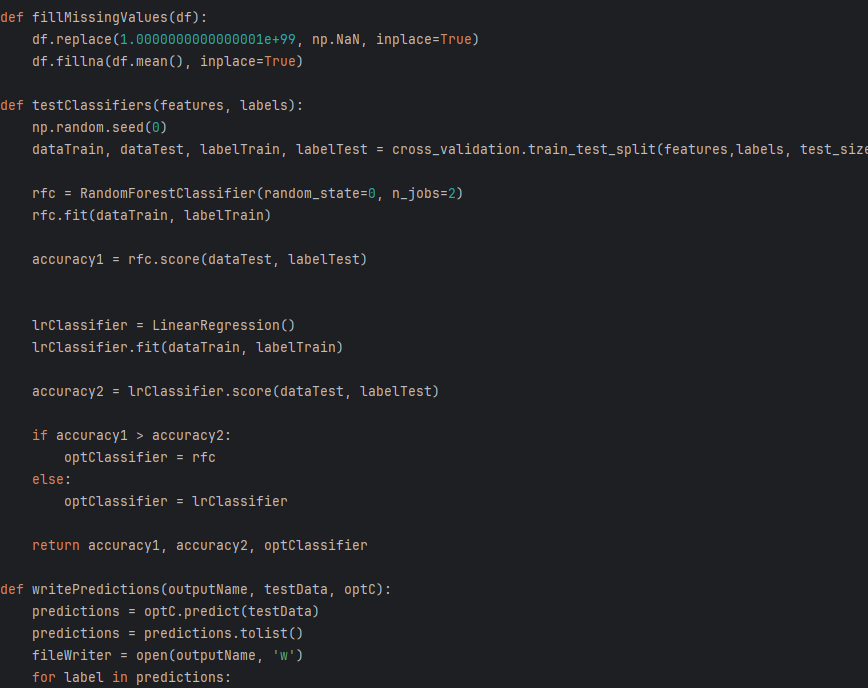
- Outlier Handling: Implemented logic to detect and replace extreme noise values (e.g., $1.0e+99$) with
NaNto prevent skewing the statistical mean. - Data Sanitization: Utilized
df.dropna()for validation sets and ensured consistent data types across the dataframe to support mathematical operations.
Automated Classification and Model Selection
The final stage of the pipeline automates the selection of the most accurate machine learning model for a given dataset.
- Model Testing: The system concurrently trains and evaluates two distinct approaches:
- Random Forest Classifier: A non-linear ensemble method utilizing multiple decision trees (
RandomForestClassifier). - Linear Regression: A standard linear approach to gauge baseline classification performance.
- Random Forest Classifier: A non-linear ensemble method utilizing multiple decision trees (
- Optimization Logic: Using
cross_validation.train_test_split, the tool measures the accuracy scores of both models. ThetestClassifiersfunction programmatically selects the "Optimal Classifier" (optClassifier) based on which method achieved the highest precision for that specific data distribution.
Outcomes
- High Efficiency: Developed a
writePredictionsutility to streamline the deployment of the selected model, converting results to optimized lists for file output. - Physics-Aware Logic: By implementing distance-based clustering from scratch (
np.sqrt(np.power(...).sum())), the project demonstrates a deep understanding of the vector math required for custom machine learning implementations beyond standard library calls.