Android Security

Summary
A security-focused mobile application researching OS-level data protection and authentication, utilizing Android Studio and Virtual Machines to implement secure password hashing and local credential persistence.
Details
This project was developed as a research-led exploration into Operating System security within the Android ecosystem. The application serves as a testbed for implementing secure user authentication workflows, focusing specifically on protecting sensitive data through robust password hashing techniques and structured local persistence.
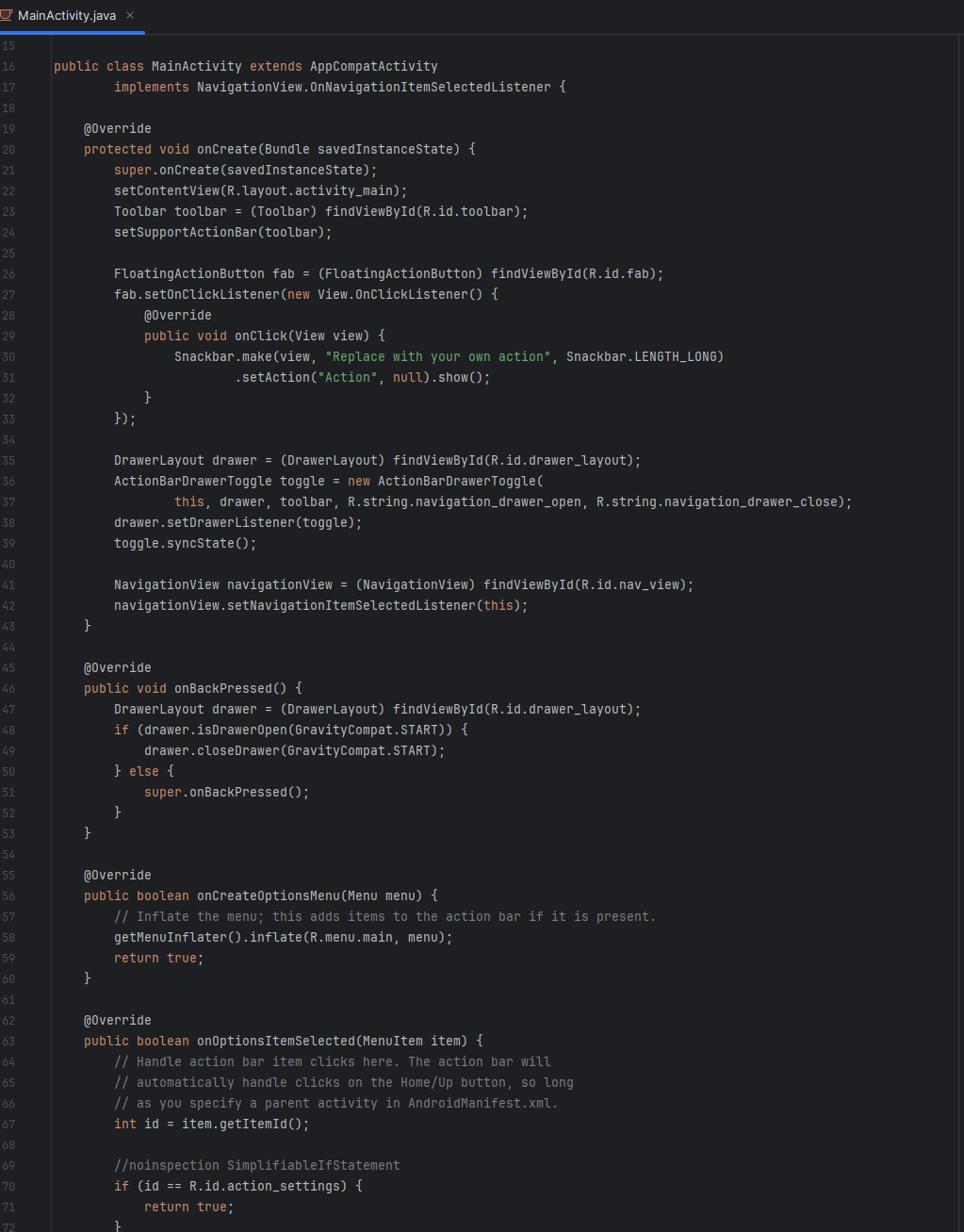
The application is built on a modular Java architecture that enforces a strict separation between user interface logic and security-focused data management. The system consists of five core Java classes and their respective XML-based layout definitions.
Activity Management & Lifecycle
The front-end logic is distributed across three primary Activity classes, each managing a specific stage of the authentication lifecycle:
- MainActivity: Serves as the primary entry point and navigation hub. I used a
NavigationViewandDrawerLayoutto architect a fluid user experience for accessing secure features. - LoginActivity: Handles credential validation against the local user database.
- CreateAccountActivity: Manages the secure onboarding of new users, serving as the interface for initial password entry and salt/hash generation.
Security and Data Persistence
The backend logic of the application focuses on the secure storage and retrieval of user identities:
- User Modeling: The
Userclass acts as a data model, defining the structure of stored credentials and ensuring type safety during data manipulation. - UserDatabase Logic: This class handles the persistence layer, interfacing with the Android OS to store hashed credentials.
- Credential Hashing: The project’s primary research focus was the implementation of hashing algorithms to ensure that passwords are never stored in plaintext, mitigating risk in the event of an OS-level data breach.
Development and Testing Environment
To simulate real-world mobile hardware constraints and test OS-level security vulnerabilities, the development process was conducted entirely through Virtual Machines and Emulator instances.
- Virtualization: Utilized VMs and Emulators to create isolated environments for testing application behavior across different Android OS versions.
- Android Studio Integration: Leveraged the Android SDK to manage layouts (XML) and standard Activity overrides (e.g.,
onCreate,onBackPressed) to ensure stable performance.
Outcomes
- Secure Authentication Flow: Successfully demonstrated a full authentication loop—from account creation and hashed storage to validation and login.
- UI/UX Integrity: Developed a multilayered user interface leveraging standard Android components like the
FloatingActionButtonandSnackbarfor real-time user feedback during secure operations. - Persistence Integrity: Verified that user data remained consistent and protected within the
UserDatabasethroughout the application lifecycle.